Feeling tired even when you’re “eating healthy”? The quiet gap is often consistent, quality protein. This guide turns Plant Based Protein Sources into real meals you can cook today—no powders required, no complicated math.
உணவில் புரதம் சரியாக கிடைத்தால் சக்தி, மன தெளிவு, இரவுநேர உறக்கம்—அனைத்தும் மேம்படும். இன்று தொடங்கலாம்.
Table of Contents
- A Gentle Reset: Why Plant Protein Works
- Common Myths About Plant Based Protein Sources
- Top 15 Plant-Based Protein Sources (Deep Dive)
- Combining Foods for Complete Amino Profiles
- Digestibility: Soak • Sprout • Pressure Cook
- Balanced Day Plate (Visual Guide)
- 7-Day Plant Protein Meal Plan (Flexible)
- Use Cases: Weight, Blood Sugar & Performance
- Protein Trios Bowl (Fast, Filling Pattern)
- Practical Tamil-Friendly Patterns
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- References
A Gentle Reset: Why Plant Protein Works
Plant Based Protein Sources offer something animal foods cannot: protein wrapped in fiber, antioxidants, potassium, magnesium, and diverse phytochemicals that quietly protect the heart and gut. When protein rides along with fiber and micronutrients, blood sugar swings flatten, satiety rises, and the “afternoon crash” fades. You do not need meat or whey at every meal to feel strong. What you need is a steady rhythm—protein at breakfast to curb cravings, protein at lunch to sustain focus, and protein at dinner to support recovery. Add a small protein-forward snack and you’ve built a day that carries you calmly from task to task.
Many readers come to this topic with a history of low-protein breakfasts (white bread, tea, sugar); lunches heavy on refined rice; and dinners that swing between too light and too oily. This plan reframes the plate: put Plant Based Protein Sources at the center, then surround them with colorful vegetables and whole grains. The texture becomes satisfying, the flavors feel grounded, and the results last beyond one week. எளிய பாட்டம்: “தட்டு” மையம்—புரதம்.
Common Myths About Plant Based Protein Sources
- “Plant proteins are incomplete, so you can’t meet your needs.”
The idea confuses “single food completeness” with “dietary completeness.” Soy stands alone as complete. But even when a single food is low in one amino acid (e.g., legumes are lower in methionine; grains are lower in lysine), the day’s pattern fixes it. Your body maintains an amino acid pool; it’s the variety of Plant Based Protein Sources across 24 hours that matters. - “You need huge amounts of protein.”
More isn’t always better. Many healthy adults thrive around 0.8–1.0 g/kg/day, distributed across meals. Heavy training or specific life stages may raise targets, but for most people, consistency beats megadoses. சீரான அளவு—தினமும்—அதுவே பலன். - “Beans always cause gas.”
Tolerance is a skill. Soak and rinse, cook thoroughly, use digestive spices (cumin, ginger, asafoetida), start with smaller portions, and allow your gut microbes two to three weeks to adapt. The payoff—fiber + protein + minerals—makes Plant Based Protein Sources worth it.
Top 15 Plant-Based Protein Sources (Deep Dive)
Use this image as your on-fridge reminder. Rotate the items to broaden micronutrients and textures.


- Lentils — Red, green, and brown cook quickly; split varieties (masoor, moong dal) are weeknight heroes. Pair with tomato, spinach, or drumstick for iron and vitamin C synergy.
- Chickpeas — Soak well and pressure cook; the cooking liquid (aquafaba) lightens egg-free bakes. In salads, add lemon and sesame for taste + calcium.
- Black beans / Kidney beans — Hearty, meal-worthy. Combine with brown rice or millet; add paprika, cumin, onions for a bowl that satisfies for hours.
- Soy (Tofu, Tempeh, Edamame) — Complete protein. Tofu soaks up marinades; tempeh brings nutty flavor and probiotics; edamame is a quick snack for 10–12 g protein per cup.
- Peas — Fresh peas add sweetness to upma or pulao; dried peas make chunky soups. Handy when you’re out of dal.
- Quinoa — Fluffy base with 8–9 g protein per cooked cup. Rinse well to reduce saponins; add roasted veg + tofu for a “power bowl.”
- Oats — Not just sweet. Try savory oats with onion, tomato, chilies, and peas; top with roasted peanuts or seeds for crunch and extra protein.
- Millets (kambu/pearl, ragi/finger, kodo) — Minerals + slow carbs. For formats and choices, see Best Millets.
- Buckwheat / Amaranth — Naturally gluten-free; great for rotis, porridge, and salad bowls. Amaranth pops like tiny nutty popcorn.
- Peanuts & Peanut Butter — Budget-friendly. Chutneys, laddus, energy bars; pair with fruit for a high-satiety snack.
- Almonds / Mixed Nuts — Vitamin E + magnesium for recovery and nerve health. Blend into smoothies or grind into chutneys.
- Seeds — Pumpkin (zinc), sunflower (vitamin E), hemp (complete), chia (omega-3), sesame/ellu (calcium). A spoonful upgrades bowls and curd.
- Greek Yogurt / Curd (or fortified plant yogurts) — Protein + probiotics. For lactose-sensitive readers, try smaller servings with meals.
- Paneer / Cottage Cheese — Quick sauté with capsicum and onions, or crumble into millet rotis for a satisfying wrap.
- Dark Leafy Greens — Spinach, amaranth, moringa leaves: modest protein but mighty minerals. Cook with dal to improve iron uptake.
Pro tip: Build “protein trios” from your favorite Plant Based Protein Sources—for example, tofu + quinoa + pumpkin seeds or chickpeas + kodo millet + spinach. Trio logic delivers protein + fiber + minerals in one bowl.
Combining Foods for Complete Amino Profiles
The reason combinations matter is simple biochemistry. Lysine is abundant in legumes, while methionine is richer in grains and seeds. When you mix them across a day, the limiting amino acid of one is complemented by the other. Soy and hemp are notable exceptions—they’re already complete—but even then, variety helps micronutrients. Classic templates:
- Legume + Grain: chana + brown rice; rajma + millet; lentil khichdi; இட்லி/தோசை + சாம்பார் (fermentation improves digestibility and flavor).
- Grain + Soy: quinoa + tofu/tempeh bowls with roasted vegetables.
- Legume + Seeds/Nuts: chickpea salad with pumpkin seeds; moong sprouts with sesame dressing.
- Dairy/fortified plant milks + Oats/Millets: breakfast parfaits and smoothies to front-load protein.
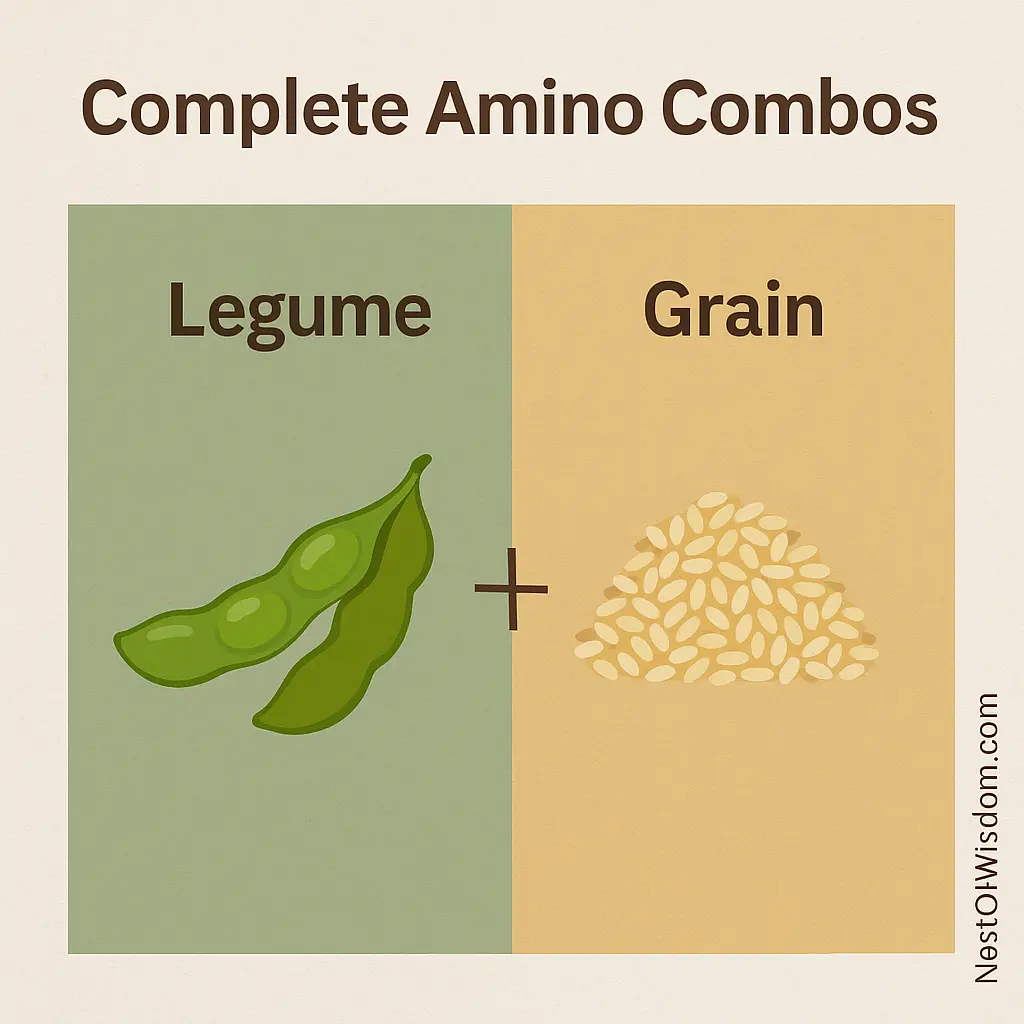

ஒரே தட்டில் எல்லாவற்றையும் சேர்க்க வேண்டிய அவசியமில்லை; think across the day, not every single plate. With diverse Plant Based Protein Sources, completeness happens naturally.
Digestibility: Soak • Sprout • Pressure Cook
Comfort determines consistency. Many stop eating beans because of discomfort—not because they dislike the taste. A few small changes keep Plant Based Protein Sources comfortable:


- Soak & rinse to reduce oligosaccharides and improve texture. Add a small pinch of baking soda only if needed and rinse well.
- Pressure cook thoroughly. Undercooked skins cause trouble; soft beans are kinder. Add ginger, cumin, ajwain, or asafoetida to support comfort.
- Sprout mung/gram 12–24 hours; lightly steam before salads if you’re new to raw sprouts. Sprouting increases certain B-vitamins and reduces antinutrients.
To further support digestion, keep hydration and fiber steady. For constipation-proofing, see High-Fiber Foods for Constipation Relief; for soothing beverages, explore Herbal Drinks for Blood Pressure. For brain-smart eating, try the MIND Diet Guide.
Balanced Day Plate (Visual Guide)
Use this visual to distribute protein steadily—your appetite and mood will notice.


7-Day Plant Protein Meal Plan (Flexible)
Think of this as a rotation, not rules. Swap within categories and adjust portions for your needs (more on that below).
Daily Pattern
- Breakfast: Oats or quinoa + nuts/seeds + fruit (or gram-flour “omelet” with vegetables). Front-loading protein blunts cravings.
- Lunch: Millet or brown rice + legume curry/dal + leafy greens. Add a probiotic side (curd or fermented veg) for gut support.
- Dinner: Tofu/tempeh + quinoa or whole-grain roti + colorful vegetables. Keep oils moderate.
- Snack: Roasted chickpeas, peanut chikki, yogurt/curd, or seed mix.
Helpful companions while you plan: grains and swaps from Healthiest Types of Rice, smart millet picks in Best Millets, and breakfast rotation ideas in Diabetic-Friendly Indian Breakfast Recipes.
Portion pointers by goal — For weight management, emphasize vegetables and dal, and use measured healthy fats. For diabetics, pair carbs with protein and fiber at every meal; avoid fruit-only snacks. For athletes, add an extra 15–25 g of protein within 1–2 hours post-workout (soy curd bowl, tofu stir-fry, peanut-banana smoothie).
Use Cases: Weight, Blood Sugar & Performance
Weight management: Protein + fiber increases satiety and lowers “food noise.” Bowls built from Plant Based Protein Sources (legume + grain + veg + seeds) reduce mindless snacking. One small habit—high-protein breakfast—often shifts total daily intake.
Blood sugar support: Pair protein with color and crunch. For glucose-friendly combos, see Low-GI Foods for Diabetics and activity support in Yoga Poses to Lower Blood Sugar. Legume-rich lunches are a quiet superpower for afternoon stability.
Performance & recovery: Distribute protein (20–30 g targets) across main meals. Soy, lentils, and peanuts provide economical, high-impact Plant Based Protein Sources. Add vitamin C foods with iron-rich legumes to support oxygen transport.
Micronutrients: Vegetarians should plan for B12 and iron—see Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Vegetarians and Iron Deficiency Natural Remedies. A small sesame or pumpkin seed sprinkle meaningfully boosts zinc and calcium.
Protein Trios Bowl (Fast, Filling Pattern)
When time is tight, assemble a trio: one legume + one grain/pseudograin + one seed/nut + vegetables. Drizzle with lemon-tahini or curd-mint dressing. The combo feels restaurant-level but takes 10–12 minutes if your beans are pre-cooked.


- Tofu + quinoa + pumpkin seeds with sautéed greens and lemon.
- Chickpeas + kodo millet + spinach with cumin and garlic.
- Lentils + savory oats + sesame with tomatoes and herbs.
Practical Tamil-Friendly Patterns
Keep favorite flavors—tune the protein. Here are high-comfort, high-protein patterns using familiar Plant Based Protein Sources:
- Idli / Dosa + Sambar — Fermented dal + rice combo naturally pairs lysine-rich legumes with methionine-rich grain. Add a peanut or sesame chutney for extra protein + minerals.
- Adai (multigrain dosa) — Channa dal, toor dal, urad dal + rice batter. Crisp edges, serious protein—perfect with avial.
- Pesarattu — Whole green gram dosa; serve with upma or ginger chutney for a complete breakfast.
- Ragi mudde + Soppu/Dal — Sustained energy from ragi + protein from greens/dal. Great field-day meal.
- Kollu (horse gram) rasam + red rice — Warming and protein-dense; sprinkle sesame for calcium.
- Sundal (chickpea/green gram) — Festival favorite turned everyday snack; finish with grated coconut and lemon.
சுவையை காப்பாற்றி, புரதத்தை உயர்த்துவது தான் குறிக்கோள். “சிறு திருத்தங்கள்—பெரிய பலன்கள்.”
FAQs
1) Can you get all essential amino acids from Plant Based Protein Sources?
Yes. Soy foods are complete by themselves; other Plant Based Protein Sources become complete when you eat a varied pattern across the day (legume + grain + seeds/nuts + dairy/fortified options).
2) How much protein do most adults need?
Many healthy adults target ~0.8–1.0 g/kg/day as a baseline, increasing with heavy training or specific life stages. Distribute Plant Based Protein Sources across meals for steadier energy and recovery.
3) Is soy safe?
For most people, traditional soy foods (tofu, tempeh, edamame) are nutritious. If you have a thyroid condition or soy allergy, follow your clinician’s advice. Soy remains one of the most convenient complete Plant Based Protein Sources.
4) I feel gassy with beans—what can I do?
Soak and rinse, pressure cook thoroughly, use digestive spices, and increase portions gradually over 2–3 weeks. Most people adapt and enjoy the benefits.
5) Are protein powders necessary on a vegetarian diet?
Optional. You can meet needs via whole-food Plant Based Protein Sources; powders help only when appetite, time, or higher targets make whole-food intake difficult.
6) What about kids and older adults?
Both can thrive on Plant Based Protein Sources with thoughtful variety and portions. Discuss individual needs with a pediatrician or dietitian for growth, recovery, or medical conditions.
7) Do Plant Based Protein Sources harm the kidneys?
No, not in healthy kidneys. Whole-food plant proteins arrive with fiber and minerals and generally produce a lower acid load. People with diagnosed kidney disease need individualized medical guidance regardless of diet pattern.
8) How do Plant Based Protein Sources compare to whey protein?
Whey is fast-digesting and useful in certain athletic contexts, but well-planned Plant Based Protein Sources can match total daily protein, while adding fiber and phytonutrients. For athletes, soy yogurt bowls, tofu stir-fries, and peanut/banana smoothies conveniently cover the gap.
Conclusion
You don’t need complicated spreadsheets or meat at every meal to feel strong. Rotate Plant Based Protein Sources—lentils, chickpeas, soy, quinoa, oats, millets, nuts, seeds—cook them well, pair them smartly, and keep portions balanced. Start with one bowl today: legume + grain + colorful veg + a sprinkle of seeds. Repeat daily, review weekly, and your energy and recovery will mirror your consistency. இன்று தொடங்கு; உடல் நன்றி சொல்லும்.
References
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health — The Nutrition Source: Protein
- USDA — Dietary Guidelines
- PubMed — Plant protein & health outcomes (search index)
Nest of Wisdom Insights is a dedicated editorial team focused on sharing timeless wisdom, natural healing remedies, spiritual practices, and practical life strategies. Our mission is to empower readers with trustworthy, well-researched guidance rooted in both Tamil culture and modern science.
இயற்கை வாழ்வு மற்றும் ஆன்மிகம் சார்ந்த அறிவு அனைவருக்கும் பயனளிக்க வேண்டும் என்பதே எங்கள் நோக்கம்.
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
Related posts
Today's pick
Recent Posts
- Internal Linking Strategy for Blogs: A Practical, Human-Centered Playbook
- AI in the Automotive Industry: A Practical, Human-Centered Guide
- Cloud Tools for Small Businesses and Freelancers: The Complete Guide
- Generative AI in Business: Real-World Use Cases, Benefits & Risks
- 7 Life-Changing Daily Habits for Weight Loss Without Dieting

