“மக்னீசியம் குறைபாடு இருண்ட அறையில் இருக்கும் மெளன அலாரம் போல—அது ஒலிக்காமல் இருப்பது தான் பிரச்சனை.” Many people walk around with unrecognized magnesium deficiency—wired yet tired, crampy, foggy, or sleeping poorly. This expanded, science-backed guide explains what magnesium does, the 15 warning signs of magnesium deficiency, exact RDA targets, the best vegetarian foods, a realistic 7-day plan, a simple daily routine, smart supplement choices, testing options, and a measurement framework you can actually follow. Bookmark this page and come back to it whenever your body needs a reset.
Table of Contents
- 1) Why Magnesium Matters
- 2) 15 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
- 3) How Much Magnesium You Need (RDA & Real-World Targets)
- 4) 21 Vegetarian Foods Rich in Magnesium
- 5) 7-Day Vegetarian Magnesium Plan (Meals & Snacks)
- 6) Daily Routine for Magnesium Balance
- 7) Sleep, Stress, Heart & Gut: How Deficiency Shows Up
- 8) Supplements: Forms, Safety & Interactions
- 9) Testing, Who’s at Risk & When to See a Doctor
- 10) Measurement Framework: KPIs & Cost Control
- 11) FAQs
- Conclusion
- References
1) Why Magnesium Matters
Magnesium is a quiet workhorse powering 300+ biochemical reactions. It stabilizes ATP (your cell’s energy currency), supports nerve conduction, relaxes muscles, regulates heart rhythm, moderates blood sugar, assists vitamin D activation, and contributes to bone structure. A mild, chronic magnesium deficiency can ripple into sleep issues, low stress tolerance, cramps, headaches, and constipation—common complaints that often improve when dietary intake rises steadily.
Why deficiency happens: low-variety diets, highly refined grains, low legume intake, soil nutrient depletion, heavy sweating, chronic GI conditions, alcohol excess, and certain medicines (PPIs, some diuretics, and specific antibiotics). தமிழில்: “சிறு குறைபாடே காலப்போக்கில் பெரிய பாதிப்பை தரலாம்”—even a small intake gap can create outsized symptoms over time.
2) 15 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency


Not everyone with magnesium deficiency has all signs, but clusters matter. Here’s how to interpret them:
- Muscle cramps or twitching—especially calves, feet, eyelids. Low magnesium impairs muscle relaxation and can amplify nerve excitability.
- Tingling or numbness—“pins and needles” from altered nerve function.
- Restless sleep—frequent awakenings, light sleep, vivid dreams. Magnesium supports GABA and overall relaxation.
- Headaches or migraines—some people notice fewer episodes after restoring intake.
- Anxiety, irritability—stress systems run hotter under deficiency; magnesium helps the “calm brake.”
- Palpitations—flutter sensations. Always get heart symptoms medically evaluated.
- Fatigue, low energy—ATP stabilization depends on magnesium; shortages can feel like a flat battery.
- Constipation—sluggish bowels often improve with fiber + fluids + better magnesium status.
- Low appetite or mild nausea—nonspecific, but can co-present with deficiency.
- Muscle weakness, slow recovery—exercise soreness lingers longer when intake is low.
- Brain fog, low mood—focus and recall feel “off.”
- Worsening PMS or cramps—common report in low magnesium states.
- Rising blood pressure trends—multifactorial; talk to your clinician.
- Electrolyte disturbances—low potassium/calcium may co-occur.
- Severe red flags—tremors, confusion. Seek urgent care.
If these patterns resonate, a steady food-first approach can correct many cases of magnesium deficiency. If symptoms persist or include heart or neurological concerns, involve a clinician early.
3) How Much Magnesium You Need (RDA & Real-World Targets)
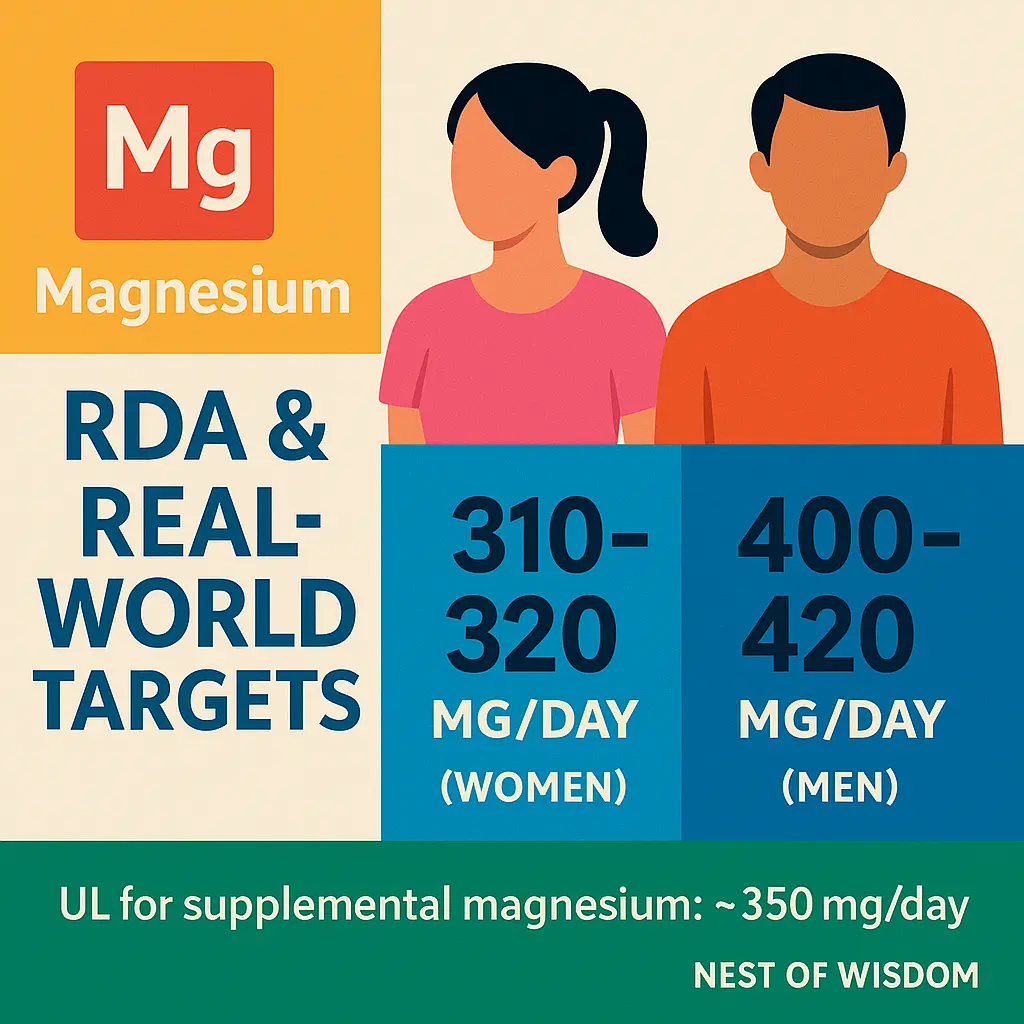

Typical adult targets: ~310–320 mg/day (women) and ~400–420 mg/day (men). Pregnancy and lactation needs are somewhat higher; older adults may require extra attention due to absorption changes. Most healthy people can meet needs with thoughtful food patterns.
Upper limit (UL) for supplements: about 350 mg/day from supplemental magnesium for most adults. Magnesium in food does not count toward the UL. “More” isn’t always “better”—excess supplemental intake can cause diarrhea, low blood pressure, or medication interactions. தமிழ் நினைவூட்டு: “அளவுக்கு மீறினால் அமிர்தமும் நஞ்சு.”
Bioavailability basics: different forms absorb differently. Magnesium citrate and glycinate are typically well tolerated; oxide has higher elemental magnesium but lower absorption for many. For sleep or anxiety, many clinicians choose glycinate; for constipation-prone individuals, citrate may help. Use supplements thoughtfully to close gaps while your diet improves—a sustainable fix for magnesium deficiency is still food.
4) 21 Vegetarian Foods Rich in Magnesium


Rotate from these vegetarian staples to raise intake steadily and keep meals interesting:
- Seeds—pumpkin, sesame (ellu), sunflower: dense, portable, and the fastest way to lift intake. Toast lightly and sprinkle over dal, salads, or yogurt.
- Nuts—almonds, cashews, peanuts: 1 small handful per day can materially move the needle.
- Leafy greens—spinach, amaranth (keerai), moringa leaves: pair with vitamin-C foods (lemon, amla) to support mineral uptake.
- Legumes—black beans, chickpeas, lentils: soak and rinse to reduce phytates; pressure cooking improves tolerance.
- Whole grains—oats, quinoa, brown/red rice (Healthiest Types of Rice): keep the bran and germ for better magnesium and fiber.
- Millets—kambu (pearl), ragi (finger), kodo, foxtail (Best Millets): the traditional Tamil pantry’s mineral powerhouses.
- Fruits & others—avocado, banana, dark chocolate (70%+), cocoa; yogurt/curd; fortified plant milks.
Bioavailability tips: soak/ferment legumes and millets; pair with vitamin C; rotate greens (not just spinach); avoid over-boiling. For digestion support and regularity (often affected by magnesium deficiency), explore High-Fiber Foods for Constipation Relief and hydration ideas in Herbal Drinks for Blood Pressure. Brain-nourishing dietary patterns also help—see the MIND Diet Guide.
5) 7-Day Vegetarian Magnesium Plan (Meals & Snacks)
“சிறு மாற்றங்கள் தினமும்—நீண்டகாலத்தில் பெரிய பலன்.” Use this practical rotation alongside your family’s tastes and budget. The goal is consistency, not perfection, while restoring a mild magnesium deficiency.
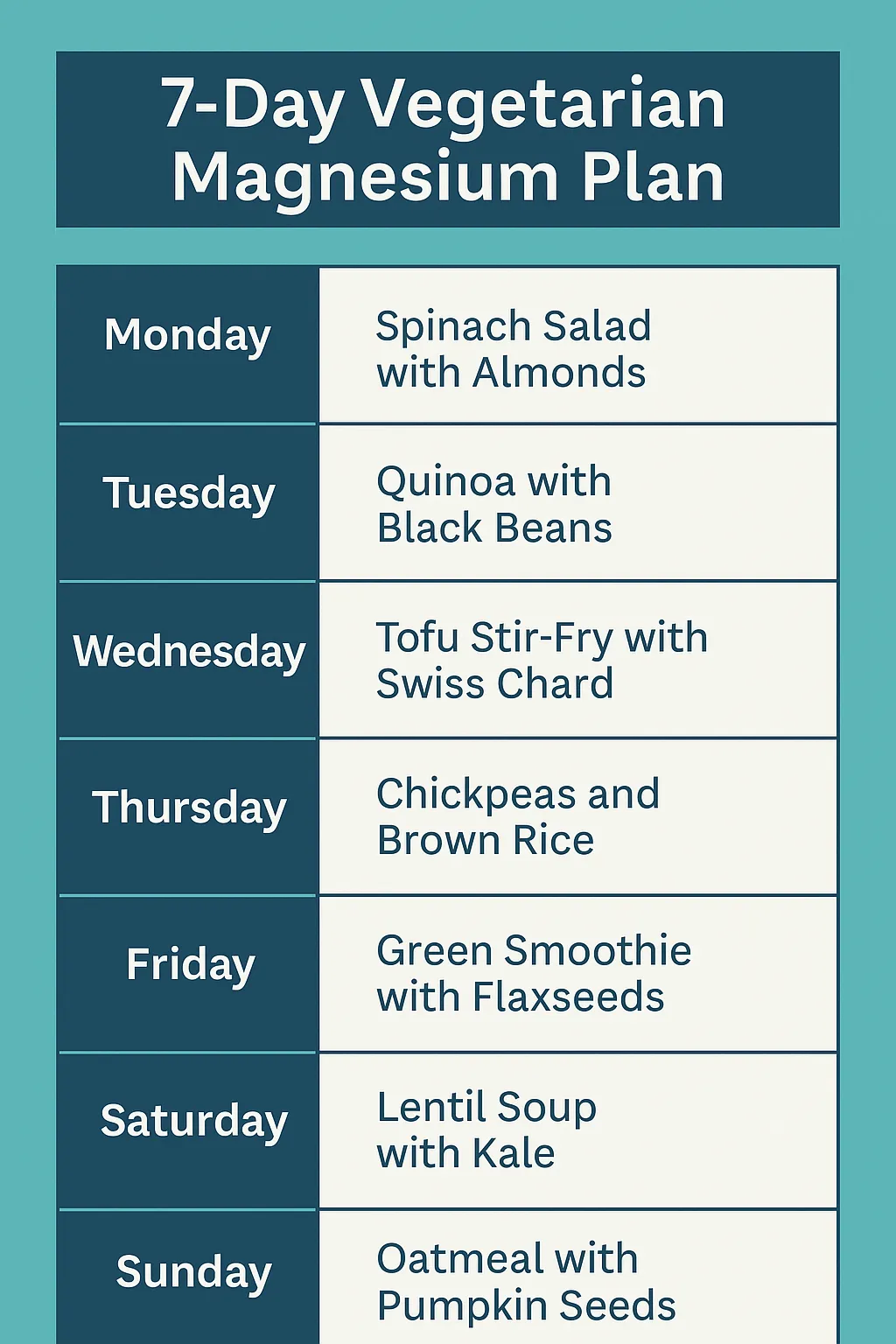

How to read the plan
- Breakfast base: oats or quinoa + nuts/seeds + fruit (banana, berries, seasonal).
- Lunch: brown/red rice or millets + legumes + leafy greens (sautéed or dal).
- Dinner: quinoa/millets + lentils/soy + colorful vegetables.
- Snacks: pumpkin/sesame/sunflower seeds, yogurt/curd, a square of dark chocolate.
Batching tips: soak and cook legumes in bulk; roast a seed mix once a week; keep frozen greens for quick stir-fries; prepare spice-free base dal you can season differently each day. These habits protect your plan on busy weeks and help reverse magnesium deficiency gently.
6) Daily Routine for Magnesium Balance


Hydration: sip water through the day; consider mineral water a few times weekly; choose herbal teas in the evening. Dehydration worsens cramps and constipation, two hallmarks of magnesium deficiency.
Breakfast: oats or quinoa + nuts & seeds; fruit on the side. This gently stabilizes blood sugar and curbs mid-morning energy dips.
Lunch: millets or brown/red rice + legumes/soy + leafy greens. Traditional South-Indian plates already align well; we’re just making them more consistent.
Movement: walks, light mobility, or yoga (cat-cow, child’s pose, seated forward fold). Gentle stretching reduces muscle tension when magnesium deficiency causes tightness.
Dinner: keep it balanced but lighter—quinoa or millets, lentils/soy, and veggies. Avoid very late heavy meals that disrupt sleep.
Wind-down & sleep: dim lights, reduce screens; keep a steady sleep window. Magnesium assists melatonin synthesis, so your improved intake pays off here. For deeper sleep practices, see Daily Habits for Better Sleep.
7) Sleep, Stress, Heart & Gut: How Deficiency Shows Up
Sleep: people with mild magnesium deficiency often report light sleep and frequent awakenings. Foods with nuts/seeds at dinner (or glycinate form supplements, if advised) plus darker evenings can help.
Stress: during hectic weeks, your body uses more magnesium. Coffee-heavy, low-variety days can reveal edginess and headaches. Try a 10-minute breathwork or a brief Tamil mantra meditation—“ஓம் சாந்தி”—to downshift.
Heart: magnesium supports normal rhythm and vascular tone. Palpitations deserve a clinician’s evaluation; don’t self-diagnose. Improving overall intake remains valuable even alongside medical care.
Gut: constipation frequently travels with magnesium deficiency. Add soluble/insoluble fiber (see our High-Fiber Foods list), hydrate, and move daily. Some find citrate form (see below) helpful under guidance.
8) Supplements: Forms, Safety & Interactions
If food changes alone don’t correct magnesium deficiency, discuss supplements with your clinician. Common forms:
- Magnesium glycinate—gentle, often used for sleep/anxiety support.
- Magnesium citrate—more laxative; may help constipation-prone individuals.
- Magnesium oxide—higher elemental Mg, lower absorption, GI upset possible in some.
- Magnesium L-threonate—marketed for cognition; evidence is still evolving.
Safety: the UL for supplemental magnesium is ~350 mg/day for most adults (food magnesium doesn’t count). Separate magnesium from certain antibiotics and thyroid medications by 2–4 hours. People with kidney disease must consult a clinician before using supplements. The objective is to resolve magnesium deficiency safely and then maintain with food.
9) Testing, Who’s at Risk & When to See a Doctor
Serum magnesium may be normal even when tissues are low, so clinicians combine history, symptoms, diet review, electrolytes, and sometimes repeat measurements. Higher-risk groups for magnesium deficiency include older adults; people with chronic GI conditions, alcohol dependence, and uncontrolled diabetes; and those on PPIs/diuretics. Seek medical advice for persistent symptoms, heart rhythm concerns, significant weakness, or before using higher-dose supplements.
10) Measurement Framework: KPIs & Cost Control
Turning around a mild magnesium deficiency is easier when you track a few basics. Use a four-week sheet with:
- Weekly symptom score—sleep quality, cramps, energy, headaches (0–10 scale).
- Food frequency—how many times per day you include seeds/nuts/greens/legumes/whole grains.
- Hydration + fiber—liters/day and bowel regularity (✔/✖).
- Cost control—bulk buy seeds; rotate legumes; use seasonal greens; cook once, eat twice.
- Sunday review—keep what works, simplify what doesn’t. தமிழில்: “ஓவ்வொரு ஞாயிற்றுக்கிழமையும் முன்னேற்றம் கணக்கிடுங்கள்.”
Pair nutrition with foundational habits that reduce the load on a body under magnesium deficiency: steady sleep windows, sunlight exposure, and light movement breaks. For broader natural supports, explore Natural Remedies for Common Health Problems. Also see Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Vegetarians and Iron Deficiency Natural Remedies—deficiencies often travel together.
11) FAQs
1) Can magnesium deficiency really cause poor sleep?
Yes. Magnesium participates in the brain’s calming pathways and makes it easier to wind down. Steady food intake plus sleep hygiene (dimmer evenings, earlier screens-off) helps many people.
2) What’s the fastest food-first way to fix magnesium deficiency?
Build each day around seeds/nuts, greens, legumes, and whole grains/millets. A simple rule: seeds daily, greens often. If needed, a gentle supplement—after medical advice—can speed the turnaround.
3) Which supplement form is best?
It depends on your goal and tolerance. Many people do well with glycinate (calming, gentle). Citrate can help constipation. Discuss options with a clinician, especially if you take regular medicines.
4) Do magnesium sprays or Epsom salt baths help?
Topical magnesium is popular, but evidence for meaningful absorption is mixed. Epsom salt baths can relax muscles and aid wind-down routines even if systemic absorption is modest. They’re a supportive habit, not a sole fix for magnesium deficiency.
5) Can children or older adults use magnesium supplements?
Possibly, but dosing and safety vary by age and health status. Always involve a healthcare professional. For many, a food-first plan corrects a mild magnesium deficiency without supplements.
Conclusion
“சீராக உணவும், அமைதியாக உறங்கவும்—அமைதியாக உடல் தன்னைச் சரிசெய்யும்.” Most people can repair a mild magnesium deficiency with small, steady steps: seeds, nuts, greens, legumes, whole grains, and millets; smart hydration; light daily movement; and consistent sleep. If symptoms persist or you notice heart rhythm issues, get tested and seek medical guidance. With a simple plan and weekly review, balance returns to nerves, muscles, heart rhythm, digestion, and energy—quietly, reliably, and sustainably.
References
- NIH Office of Dietary Supplements – Magnesium (Consumer)
- NIH Office of Dietary Supplements – Magnesium (Health Professional)
- Harvard Health – What you should know about magnesium
- Harvard Health – What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need? (2025)
- A Comprehensive Review on Understanding Magnesium Disorders (2024)
Related reading on Nest Of Wisdom
- High-Fiber Foods for Constipation Relief
- Healthiest Types of Rice
- Best Millets
- Herbal Drinks for Blood Pressure
- MIND Diet Guide
- Daily Habits for Better Sleep
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Vegetarians
- Iron Deficiency Natural Remedies
- Natural Remedies for Common Health Problems
Nest of Wisdom Insights is a dedicated editorial team focused on sharing timeless wisdom, natural healing remedies, spiritual practices, and practical life strategies. Our mission is to empower readers with trustworthy, well-researched guidance rooted in both Tamil culture and modern science.
இயற்கை வாழ்வு மற்றும் ஆன்மிகம் சார்ந்த அறிவு அனைவருக்கும் பயனளிக்க வேண்டும் என்பதே எங்கள் நோக்கம்.
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
- Nest of Wisdom Authorhttps://nestofwisdom.com/author/varakulangmail-com/
Related posts
Today's pick
Recent Posts
- Internal Linking Strategy for Blogs: A Practical, Human-Centered Playbook
- AI in the Automotive Industry: A Practical, Human-Centered Guide
- Cloud Tools for Small Businesses and Freelancers: The Complete Guide
- Generative AI in Business: Real-World Use Cases, Benefits & Risks
- 7 Life-Changing Daily Habits for Weight Loss Without Dieting

